If some content is hidden in phone view then rotate your phone screen to landscape either or use desktop mode.
Q1. What is Polymorphism?
Polymorphism is briefly described as “one interface, many implementations”. Polymorphism is a characteristic of being able to assign a different meaning or usage to something in different contexts – specifically, to allow an entity such as a variable, a function, or an object to have more than one form. There are two types of polymorphism:
- Compile time polymorphism
- Run time polymorphism
Compile time polymorphism is method overloading whereas Runtime time polymorphism is done using inheritance and interface.
Q2. What is runtime polymorphism or dynamic method dispatch?
In Java, runtime polymorphism or dynamic method dispatch is a process in which a call to an overridden method is resolved at runtime rather than at compile-time. In this process, an overridden method is called through the reference variable of a superclass. Let’s take a look at the example below to understand it better.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 | class Car {void run(){System.out.println(“car is running”); }}class Audi extends Car {void run(){System.out.prinltn(“Audi is running safely with 100km”);}public static void main(String args[]){Car b= new Audi(); //upcastingb.run();}} |
Q3. What is abstraction in Java?
Abstraction refers to the quality of dealing with ideas rather than events. It basically deals with hiding the details and showing the essential things to the user. Thus you can say that abstraction in Java is the process of hiding the implementation details from the user and revealing only the functionality to them. Abstraction can be achieved in two ways:
- Abstract Classes (0-100% of abstraction can be achieved)
- Interfaces (100% of abstraction can be achieved)
Q4. What do you mean by an interface in Java?
An interface in Java is a blueprint of a class or you can say it is a collection of abstract methods and static constants. In an interface, each method is public and abstract but it does not contain any constructor. Thus, interface basically is a group of related methods with empty bodies. Example:
Q5. What is the difference between abstract classes and interfaces?
| Abstract Class | Interfaces |
|---|---|
| An abstract class can provide complete, default code and/or just the details that have to be overridden | An interface cannot provide any code at all, just the signature |
| In the case of an abstract class, a class may extend only one abstract class | A Class may implement several interfaces |
| An abstract class can have non-abstract methods | All methods of an Interface are abstract |
| An abstract class can have instance variables | An Interface cannot have instance variables |
| An abstract class can have any visibility: public, private, protected | An Interface visibility must be public (or) none |
| If we add a new method to an abstract class then we have the option of providing default implementation and therefore all the existing code might work properly | If we add a new method to an Interface then we have to track down all the implementations of the interface and define implementation for the new method |
| An abstract class can contain constructors | An Interface cannot contain constructors |
| Abstract classes are fast | Interfaces are slow as it requires extra indirection to find the corresponding method in the actual class |
Q6. What is inheritance in Java?
Inheritance in Java is the concept where the properties of one class can be inherited by the other. It helps to reuse the code and establish a relationship between different classes. Inheritance is performed between two types of classes:
- Parent class (Super or Base class)
- Child class (Subclass or Derived class)
A class which inherits the properties is known as Child Class whereas a class whose properties are inherited is known as Parent class.
Q7. What are the different types of inheritance in Java?
Java supports four types of inheritance which are:
- Single Inheritance: In single inheritance, one class inherits the properties of another i.e there will be only one parent as well as one child class.
- Multilevel Inheritance: When a class is derived from a class which is also derived from another class, i.e. a class having more than one parent class but at different levels, such type of inheritance is called Multilevel Inheritance.
- Hierarchical Inheritance: When a class has more than one child classes (subclasses) or in other words, more than one child classes have the same parent class, then such kind of inheritance is known as hierarchical.
- Hybrid Inheritance: Hybrid inheritance is a combination of two or more types of inheritance.
Q8. What is method overloading and method overriding?
Method Overloading :
- In Method Overloading, Methods of the same class shares the same name but each method must have a different number of parameters or parameters having different types and order.
- Method Overloading is to “add” or “extend” more to the method’s behavior.
- It is a compile-time polymorphism.
- The methods must have a different signature.
- It may or may not need inheritance in Method Overloading.
Let’s take a look at the example below to understand it better.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 | class Adder {Static int add(int a, int b){return a+b;}Static double add( double a, double b){return a+b;}public static void main(String args[]){System.out.println(Adder.add(11,11));System.out.println(Adder.add(12.3,12.6));}} |
Method Overriding:
- In Method Overriding, the subclass has the same method with the same name and exactly the same number and type of parameters and same return type as a superclass.
- Method Overriding is to “Change” existing behavior of the method.
- It is a run time polymorphism.
- The methods must have the same signature.
- It always requires inheritance in Method Overriding.
Let’s take a look at the example below to understand it better.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | class Car {void run(){System.out.println(“car is running”); }Class Audi extends Car{void run(){System.out.prinltn("Audi is running safely with 100km");}public static void main( String args[]){Car b=new Audi();b.run();}} |
Q9. Can you override a private or static method in Java?
You cannot override a private or static method in Java. If you create a similar method with the same return type and same method arguments in child class then it will hide the superclass method; this is known as method hiding. Similarly, you cannot override a private method in subclass because it’s not accessible there. What you can do is create another private method with the same name in the child class. Let’s take a look at the example below to understand it better.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 | class Base {private static void display() {System.out.println("Static or class method from Base");}public void print() {System.out.println("Non-static or instance method from Base");}class Derived extends Base {private static void display() {System.out.println("Static or class method from Derived");}public void print() {System.out.println("Non-static or instance method from Derived");}public class test {public static void main(String args[]){Base obj= new Derived();obj1.display();obj1.print();}} |
Q10. What is multiple inheritance? Is it supported by Java?
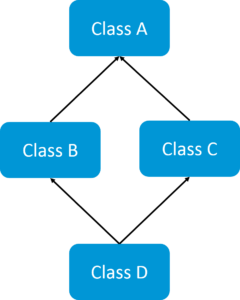 If a child class inherits the property from multiple classes is known as multiple inheritance. Java does not allow to extend multiple classes.
If a child class inherits the property from multiple classes is known as multiple inheritance. Java does not allow to extend multiple classes.
The problem with multiple inheritance is that if multiple parent classes have the same method name, then at runtime it becomes difficult for the compiler to decide which method to execute from the child class.
Therefore, Java doesn’t support multiple inheritance. The problem is commonly referred to as Diamond Problem.
In case you are facing any challenges with these java interview questions, please comment on your problems in the section below.
Q11. What is encapsulation in Java?
Encapsulation is a mechanism where you bind your data(variables) and code(methods) together as a single unit. Here, the data is hidden from the outer world and can be accessed only via current class methods. This helps in protecting the data from any unnecessary modification. We can achieve encapsulation in Java by:
- Declaring the variables of a class as private.
- Providing public setter and getter methods to modify and view the values of the variables.
Q12. What is an association?
Association is a relationship where all object have their own lifecycle and there is no owner. Let’s take the example of Teacher and Student. Multiple students can associate with a single teacher and a single student can associate with multiple teachers but there is no ownership between the objects and both have their own lifecycle. These relationships can be one to one, one to many, many to one and many to many.
Q13. What do you mean by aggregation?
An aggregation is a specialized form of Association where all object has their own lifecycle but there is ownership and child object can not belong to another parent object. Let’s take an example of Department and teacher. A single teacher can not belong to multiple departments, but if we delete the department teacher object will not destroy.
Q14. What is composition in Java?
Composition is again a specialized form of Aggregation and we can call this as a “death” relationship. It is a strong type of Aggregation. Child object does not have their lifecycle and if parent object deletes all child object will also be deleted. Let’s take again an example of a relationship between House and rooms. House can contain multiple rooms there is no independent life of room and any room can not belongs to two different houses if we delete the house room will automatically delete.
Q15. What is a marker interface?
A Marker interface can be defined as the interface having no data member and member functions. In simpler terms, an empty interface is called the Marker interface. The most common examples of Marker interface in Java are Serializable, Cloneable etc. The marker interface can be declared as follows.
1 2 | public interface Serializable{} |
Q16. What is object cloning in Java?
Object cloning in Java is the process of creating an exact copy of an object. It basically means the ability to create an object with a similar state as the original object. To achieve this, Java provides a method clone() to make use of this functionality. This method creates a new instance of the class of the current object and then initializes all its fields with the exact same contents of corresponding fields. To object clone(), the marker interface java.lang.Cloneable must be implemented to avoid any runtime exceptions. One thing you must note is Object clone() is a protected method, thus you need to override it.
Q17. What is a copy constructor in Java?
Copy constructor is a member function that is used to initialize an object using another object of the same class. Though there is no need for copy constructor in Java since all objects are passed by reference. Moreover, Java does not even support automatic pass-by-value.
Q18. What is a constructor overloading in Java?
In Java, constructor overloading is a technique of adding any number of constructors to a class each having a different parameter list. The compiler uses the number of parameters and their types in the list to differentiate the overloaded constructors.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | class Demo{int i;public Demo(int a){i=k;}public Demo(int a, int b){//body}} |
Exception and Thread Java Questions for Exam





13 Comments
Nice Blog. Thanks for sharing with us. Such amazing information.
ReplyDeleteHow is the College of Engineering Roorkee for CSE, and how are its placements?
Thanks for this very informative content.
ReplyDeleteThanks for informative content please keep it up and give us such more informative content. Please also check this BBA Admission 2025
ReplyDeleteThanks for informative content please keep it up and give us such more informative content. Please also check this BCA Admission 2025
ReplyDeleteThanks for informative content please keep it up and give us such more informative content. Please also check this PGDM Admission 2025
ReplyDeleteThanks for informative content please keep it up and give us such more informative content. Please also check this Artificial Intelligence Engineering Admission 2025
ReplyDeleteThanks for informative content please keep it up and give us such more informative content. Please also check this IoT Engineering Admission 2025
ReplyDeleteThanks for informative content please keep it up and give us such more informative content. Please also check this AI ML Engineering Admission 2025
ReplyDeleteThanks for informative content please keep it up and give us such more informative content. Please also check this Cyber Security Engineering Admission 2025
ReplyDeleteThanks for informative content please keep it up and give us such more informative content. Please also check this B.Pharm Admission 2025
ReplyDeleteThanks for informative content please keep it up and give us such more informative content. Please also check this D. Pharm Admission 2025
ReplyDeleteThanks for informative content please keep it up and give us such more informative content. Please also check this MBA Admission 2025
ReplyDeleteThanks for informative content please keep it up and give us such more informative content. Please also check this Law Admission 2025
ReplyDeleteTell us your queries or more topics which you want